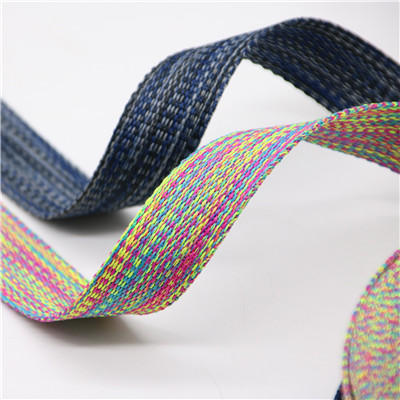
The difference between knitting and woven
The materials for webbing have gradually developed to nylon, vinylon, polyester, polypropylene, spandex, viscose, etc., forming three types of technical technologies for elastic belt weaving, knitting, and knitting. The fabric structure includes plain weave, twill weave, satin weave, jacquard, and double layers. , Multi-layer, tubular and joint arrangements.
1. The composition of the fabric arrangement:
(1) Knitted fabric: the yarn is twisted into loops in the sequence, and the loops are intertwined to form a fabric, and the process of forming loops by the yarns can be carried out horizontally or vertically. The horizontal weaving is called weft woven fabric, and the longitudinal weaving It is called warp woven fabric.
(2) Woven fabric: It is a fabric made of two or more sets of straight yarns interlaced with each other at a 90-degree angle. The longitudinal yarns are called warp yarns, and the horizontal yarns are called weft yarns.
2. The basic unit of fabric arrangement:
(1) Knitted fabric: The loop is the smallest basic unit of the knitted fabric, and the loop is formed by a space curve formed by the loop stem and the extension line.
(2) Woven fabric: Each intersection point between warp and weft is called an arrangement point, which is the smallest fundamental unit of woven fabric.
3. Fabric arrangement characteristics:
(1) Knitted fabric: Because the loops are made of yarn twists in space, and each loop is composed of one yarn, when the knitted fabric is subjected to external tension, such as longitudinal stretching, the twists and turns of the loops change, and the loops The height of the loop is also increased, but the width of the loop is reduced. If the tension is horizontal stretch, the situation is the opposite. The height and width of the loop can obviously be changed under different tension conditions, so the stretchability of the knitted fabric is large.
(2) Woven fabric: Because the warp and weft are interlaced with some twists and turns, and the moraine twists in the direction straight to the plane of the fabric, the degree of twists and turns is related to the tension between the warp and weft yarns and the stiffness of the yarn. External tension, for example, when the warp yarn is stretched in the longitudinal direction, the tension of the warp yarn is added, and the twists and turns are reduced, while the twists and turns of the weft yarn are added, such as the longitudinal stretching, until the warp yarn is completely straightened and stopped, and the fabric is shortened horizontally. When the woven fabric is stretched horizontally by external tension, the tension of the weft yarn increases, and the twists and turns are reduced, and the warp yarn twists and turns, such as horizontal stretching, until the weft yarn is completely straightened and stopped, and the fabric is longitudinally shortened. The warp and weft yarns will not change, unlike knitted fabrics.
Fourth, the characteristics of the fabric arrangement:
(1) Knitted fabric: It can extend in all directions and has good elasticity. Because the knitted fabric is composed of hole-shaped loops, it has a large air permeability function and a soft feel.
(2) Woven fabric: Because the warp and weft of the woven fabric have little relationship with the extension and shortening, and no change occurs, the fabric is generally tight and stiff.
5. Physical and mechanical properties of fabric arrangement:
(1) Knitted fabric: the physical and mechanical properties of the fabric, including vertical density, horizontal density, square meter weight, extension function, elasticity, breaking strength, abrasion resistance, curling, thickness, dispersibility, shortening, and hiding Sex, bulk density.
(2) Woven fabric: The physical and mechanical properties of woven fabric, including the yarn density of warp and weft, selvage, front and discord, forward and reverse wool direction, and fabric concealment.